This page introduces our environmental contributions and activities for biological diversity conservation.
Environmental Initiatives
Basic Policy on Environmental Information Disclosure
The Advantest Group discloses information on environmental burdens and
environmental protection activities by including such information in
our reports and website, holding exhibitions, and so forth.
We believe it is important to share environmental information with our
stakeholders and to reflect such information in our environmental
management in order to continuously grow as a company without
compromising our integrity.
We also engage in communication with local communities through various
environmental protection activities.
Number of environmental compliance initiatives
-
*Aggregation scope: Advantest Group
Environmental Information Disclosure
Environmental Contribution Activities
We endeavor to foster communication with a variety of stakeholders through environmental contribution activities.
Food recycling
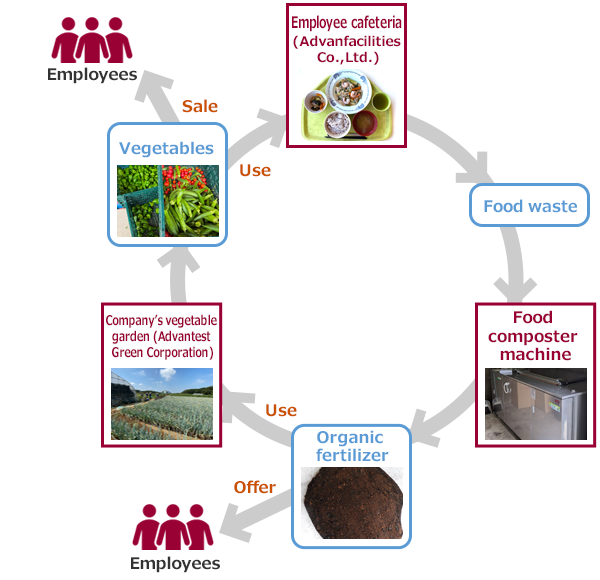
Having updated the food composter machines in September 2020, the Gunma R&D Center engages in food recycling by composting kitchen waste from the employee cafeterias of three facilities in Gunma and Saitama prefectures. Processed garbage is converted into compost, which is provided to interested employees free of charge. After the compost matures, it is used to grow vegetables on our farm, which stretches over approximately 2,000m2 of the premises of the Gunma R&D Center. On our farm, employees of Advantest Green grow pesticide-free vegetables throughout the year, and harvested vegetables are used in dishes served at the cafeterias run by Advanfacilities. We also make these vegetables available to our employees to purchase.
Advantest thus promotes employee health while reducing food waste and implementing food recycling in collaboration with affiliated companies.
the Gunma R&D Center

Environmental Impact Assessment
Advantest records and assesses the environmental burden on the area
surrounding its business establishments, such as office waste water,
in accordance with ordinances and pollution control agreements.
In addition, we are managing plants and cultivating biotope at our
business establishments while considering biodiversity.
Initiatives for Biodiversity
As stated in the “Third Mid-term Management Plan (MTP3, FY2024-2026)”, Advantest is developing initiatives for biodiversity with a focus on contributing to a sustainable global environment. Having recognized the importance of biodiversity in supporting a prosperous and healthy society, we will work to meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, based on the “Advantest Group's Guidelines of Action for Biodiversity”. Meanwhile, we will also work to expand the value we provide to our stakeholders in a balanced and multifaceted manner.
In addition, through our biotope established at the Gunma R&D Center, which is one of the largest biotopes of any private company in Japan, we will strive to earn the trust of our stakeholders by communicating with local residents, learning about the importance of the global environment, and further strengthening our awareness of our contribution to a sustainable global environment.
The Advantest Group's Guidelines of Action for Biodiversity
To show our gratitude for the gift of nature created by biodiversity, and to recognize the significance of biodiversity in supporting the prosperity and the wellness of our society, the Advantest Group will carry out initiatives in conserving biodiversity and in contributing to the sustainable use of biological resources.
-
1.Understanding Environmental Impact
We identify, evaluate and share information on any aspect that may have a significant impact on biodiversity in the entire lifecycle of our business activities. -
2.Understanding Biodiversity
We increase awareness and understanding of biodiversity among all employees so that they are able to engage in activities that give consideration to biodiversity in their business activities and daily lives. -
3.Reduction of Environmental Impact
By seeking highly effective measures, and by carrying them out continuously, we reduce the impact of our business activities on biodiversity. -
4.Cooperation with Stakeholders
We cooperate with a variety of stakeholders such as the government, educational organizations, NPOs, local residents and our business partners to promote activities related to the conservation of biodiversity.
Participation in the 30by30 Alliance for Biodiversity
Since April 2022, Advantest has joined the 30by30 Alliance for Biodiversity, a coalition of volunteer companies incorporated in the 30by30 Roadmap formulated by the Ministry of the Environment.

Initiatives for the Biotope
Reflecting our commitment to living in harmony with nature, Advantest established a biotope in Gunma R&D Center in 2001 with the aim of helping to recreate the original, natural landscape of the Kanto Plain, a landscape that is being lost to development. This biotope, with a total area of 17,000 m2, is one of the largest of its kind established by any private company in Japan.
Advantest's biotope provides a venue in which Advantest employees can learn about the importance of protecting the global environment; the biotope is also used as a way to foster communication with local residents. More than 20 years have passed since the establishment, and the biotope now has an optimal environment for preserving the local ecological system and is playing a great role in protecting and growing threatened species. The total number of plant species recorded since the establishment of the biotope has exceeded 500. In addition, Advantest's biotope provides an ideal environment for achieving an SDG target, "Goal 15: LIFE ON LAND".
-
*Biotope: This word combines the Greek words "Bio", which means life, and "Tope", which means a place.



Cooperation with Local Communities
Participation in Gunma Biotope Forum
Advantest has been participating in the Gunma Biotope Forum since 2017. This forum is organized by Professor Shin-ichi Ishikawa, Faculty of Information Science, Gunma University. Under his guidance and advice, companies and organizations in Gunma Prefecture that are engaged in biodiversity conservation gather to share information and exchange opinions.
The fiscal 2024 forum was held at the Kanto Plant (Tatebayashi City, Gunma Prefecture) of Toyo Suisan Kaisha, Ltd. on October 28. A total of 20 representatives from member companies, organizations, and Gunma University participated in the forum, reporting on their biotope-related activities and exchanging opinions. Advantest made a presentation on our biotope, including its plant and animal monitoring survey, use of fallen leaves and dead branches, our own farm, and the role of employment for people with disabilities.

Biotope Observation Classes
As part of our communication with the local community, Advantest has conducted biotope tours for elementary schools near our business sites every year since 2005, except for the year of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
In September 2025, we invited 42 first graders and their parents from a nearby elementary school to observe underwater life in the biotope pond and catch insects. On the day of the event, an employee certified as a biotope manager served as a guide, and the children enjoyed interacting with nature while searching for butterflies, dragonflies, and other creatures.
In the pond, the children observed and painted lake prawns, freshwater shrimps, and gobies caught in the traps, and then returned them to the pond apart from the lake prawns. Through these activities, participants experienced the role of the biotope based on the concept of a satoyama, a landscape shaped by human stewardship of our natural inheritance, providing an opportunity to think about biodiversity.
We will continue to collaborate with local communities to expand opportunities for people to engage with nature conservation and biodiversity.


Joint Research Project with Gunma University
Results of the 2024 Biotope Survey in the Joint Research with Gunma University
Collaborating with Professor Shin-ichi Ishikawa, Faculty of Information Science, Gunma University, we have been monitoring our biotope annually.
In the 2024 survey, 159 plant species (119 native and 40 non-native) were found to be growing in the biotope, indicating that the flora is being maintained in a stable manner. An endangered species, Eupatorium japonicum have been growing naturally in the biotope, but it did not flower in these years because of heavy grazing by some insects. To protect the plants, we set a plastic net in 2022. As a result, in 2022, one plant flowered and bore fruit in the fall and three plants flowered in 2023. Additionally, plant seeds collected in 2022 were sown and successfully germinated, with approximately 25 plants progressing to transplanting stage by 2024. In April 2025, about 70 Eupatorium japonicum seedlings were transplanted near the pond at varying distances from the water's edge, and a monitoring was conducted to track their survival and growth. By September, seedlings closer to the water edge grew larger and flowered.
Estimations of CO2 fixation by the biotope forests are conducted every five years, with the next measurement schedules for FY2026.
The net visible in the background protects the Eupatorium japonicum

growth by Gunma University

Fieldwork Course with Gunma University
From August 26 to 28, 2024, a three-day fieldwork class conducted by students from Faculty of Information Science, Gunma University, was held at the Gunma R&D Center's biotope and Gunma University's Aramaki Campus. This was part of a Project-Based Learning (PBL) under the coaching by Professor Shin-ichi Ishikawa and entitled “Restoration of regional nature using an artificial vegetation in a corporate premises.” The survey aimed to estimate CO2 fixation rates and others by trees established in our biotope.
On the first day at Gunma University, our company representatives informed our business activities and biotope initiatives. On the second day, students measured the diameter at breast height (DBH) of numerous trees in our biotope (measured at approximately 1.5 meters above ground level). Then some formulas developed by prior researches were applied to these measurements to calculate CO2 fixation rates. On the final day, students presented findings confirming that tree growth continued and CO2 fixation increased, followed by feedback from Advantest.
Students also submitted numerous proposals for future biotope utilization, including improving walking paths, creating areas to enjoy insect sounds, and conducting drone surveys. This fieldwork provided an opportunity to reaffirm the importance of biodiversity conservation and the significance of a biotope open to the local community and our employees.
Moving forward, Advantest will continue to utilize the biotope as a learning space for students who will lead the next generation. We will collaborate with local communities and educational institutions to promote environmental education and activities contributing to biodiversity conservation.

Biotope videos released
Advantest began making videos of our biotope and publishing them on our website since fiscal 2022. The videos introduce the biotope that is rich in nature, with beautiful aerial images taken by a drone of the indigenous flora and fauna that live there. These images help communicate the biodiversity of our biotope, that leads to securing a nature-positive world, to our stakeholders in an easy-to-understand manner.
Please click on the Biotope Quarterly link below to watch the biotope videos.
Place for conservation and cultivation of endangered plants
Since the establishment of the Advantest biotope in 2001, we have been conducting monitoring, and conservation of the flora and fauna and cultivation of some endangered plants inhabiting in the biotope, as well as exclusion of invasive species, under the guidance of Gunma University. We also have been conducting intensive conservation by cultivating Eupatorium japonicum and Nymphoides peltata, which are ranked as national near-threatened species and endangered (IA) species by Gunma prefecture.
There are only five sites, including the Advantest biotope, remained in Gunma Prefecture, in which Eupatorium japonicum, naturally inhabits. So our long-term intensive action of conservation by cultivating this species must provide its sustainable habitat.
Nymphoides peltata has been successfully cultivated in the biotope since 2012, for there is only one habitat for this species remained in Gunma Prefecture.
Amsonia ellipticas, ranked as national near-threatened species and endangered (IA) species by Gunma prefecture, has also been successfully cultivated in the biotope since 2019, for there is only one habitat for this species remained in Gunma Prefecture. The monitoring of this cultivation by Gunma University in September 2025 confirmed sustainable growth.



Goshawks Identified in the Biotope
In January 2024, we identified two goshawks, birds of prey, in our biotope. Since behavior consistent with those of a pair was observed, they may have been looking for a place to build a nest. They reappeared again in 2025, suggesting that they continue to use the biotope as a feeding ground.
Goshawks are rare species occupying the apex of the ecological pyramid, and their arrival serves as a vital indicator that the local natural environment is stable. In fact, the presence of goshawks has been observed to cause other bird species to temporarily disappear, creating new dynamics within the biotope's ecosystem.
These changes demonstrate that our biotope provides an attractive and safe environment for diverse organisms, serving as clear evidence that our efforts toward biodiversity conservation are steadily yielding fruitful results.
and resting in the pond.
